The age of affordable and sustainable energy solutions is upon us. And when it comes to renewable energy, solar power systems have emerged as a bright beacon of hope for a greener future. The beauty of solar energy lies in its simplicity. It harnesses the sun’s abundant energy to produce electricity, making it a reliable and renewable source of power that can drive our homes and businesses for years to come.
But how do these systems work? What are the main components of a solar power system, and how do they work together to maximise energy production and efficiency? In this article, we’ll deeply dive into solar power systems. We’ll explore the different types of solar panels and inverters, discuss the importance of batteries and charge controllers, and shed light on the many benefits of a solar power system. From reducing your carbon footprint to lowering your energy bills, solar power systems are a smart investment for anyone looking to go green and save money in the long run. So, without further ado, let’s get started!
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Case Study: Optimising a Residential Solar Power System
- 3 Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About the Main Components of a Solar Power System
- 4 Discover the Power of Solar with Solar Panels Network
- 5 Final Thoughts
Key Takeaways
- A solar power system consists of several essential components, including solar photovoltaic panels, solar inverters, racking and mounts, solar batteries, charge controllers, and a solar power meter.
- Solar panels come in various types, such as monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels. Each type is efficient and suitable for different applications, like residential or commercial setups.
- The efficiency and performance of a solar power system depend on factors like the choice of components, location, environmental conditions, sunshine hours, and electricity load requirements. Making well-informed decisions about these components is crucial for maximising the benefits of solar energy.
Component 1: Solar Photovoltaic Panel
Do you remember the shiny reflection on glass panes in a solar energy system?
These are the combination of multiple photovoltaic cells that enable solar energy conversion into electricity. Each solar system carries several PV panels for power generation, forming a solar array.
Solar panels are generally installed on the roof for maximum insolation. However, depending upon the adjustability and portability of the solar panels, they can be fixed on top of a vehicle or ground-mounted. In addition, these components are placed at an optimal angle to ensure high absorption of sunlight throughout the day.

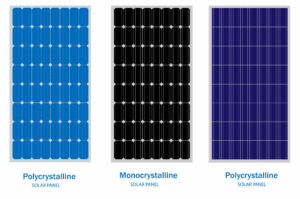
There are various types of solar panels made out of different materials. Most modern solar PV arrays are created using crystalline silicon wafers. Depending on the layers of crystal used, these panels are further divided into:
Monocrystalline Silicon Panels
The commonly known silicon cells are monocrystalline solar panels. They are called so because of the usage of a single source of silicon fused to create silicon solar cells in the panel. Since it utilises only one form of silicon, the overall efficiency of each panel increases as against the multi-crystal structure.
Due to their higher output, these solar cells are widely used in commercial projects.
Polycrystalline Silicon Panels
These panels use many small silicon crystals melted together. These crystals are termed grains separated by boundaries in the solar panel structure. These grains vary in size, ranging from nanometres to millimetres.
These are budget-friendly options but usually offer lesser efficiency than monocrystalline panels. Due to their affordability, polycrystalline silicon panels are the most preferred choice in solar power setups in residential spaces.
Thin-film Solar Cells
The thin film solar PV cells are the oldest type of cells made using amorphous silicon. They are made with noncrystalline silicon grains, unlike the usual silicon-cell wafers.
Amorphous silicon is a pocket-friendly material. However, the noncrystalline solar grains are less efficient than the monocrystalline and polycrystalline variants.
Because of the noncrystalline component, these cells can help create flexible solar panels. These solar cells generally come in handy for designing portable solar panels like RV solar systems, camping solar power generators, etc.
Component 2: Solar Inverters
Solar inverters are one of the most critical parts of a renewable energy generator with sunlight. It facilitates the conversion of DC electricity into alternating current electricity.
The conversion is crucial as most home appliances run on AC power. Even though certain equipment is available that can operate using DC electricity, they’d require additional investment from your end. The solar inverters turn the DC supply into 115, 220, or 240V current usable forms.
Depending upon the mount area and location, there are different kinds of inverters available, including:
String inverter
One can install these inverting devices onto a wall and acquire energy from a string of panels to convert them into AC electricity. They are more common in residential spaces.
Since they’re ‘centrally’ connected with the series of solar panels, they ensure optimisation of acquired power and equal efficiency distribution for each panel. However, this also proves to be a drawback for the string inverter as the dysfunction of one panel leads to the stoppage of the flow of electricity from others.
Microinverters
Like its name, these small-sized inverters are attached to each panel for converting DC power into AC electricity. Instead of aggregating the overall system’s performance, they enhance each panel’s output individually.
Due to the instalment in each panel component, the performance of the rest of the panels isn’t affected during partial shade. So, these inverters are the best choice in the solar energy system for areas severely affected by weather conditions.
Power Optimisers
These conversion systems in a solar power setup are module-level power electronics to enhance power output and efficiency. It is a DC-DC converter which is attached to each panel. Instead of converting DC electricity into AC power, these systems optimise the performance of each panel before transmitting the output to a string inverter.
They minimise the impact of weather conditions and shading on the system performance and offer high panel monitoring. These setups are responsible for aggregating the entire output of a solar panel system.

Component 3: Racking and Mounts
Besides the technical aspect of a solar panel system, the mounting structure is important to note for maximum insolation absorption. The mounting panels or gear ensure the safe and proper installation of the panels on the roof, ground or vehicle.
The quality and the material used in the rack construction are extremely important. Since the solar panels are attached outdoors, they face the brunt of extreme weather. That’s why it’s important to purchase gear which is not only strong but also corrosion-resistant.
Depending on the application area, the mounts are of three kinds:
Roof mounts
These typical mounting structures are attached to the roof’s surface for solar panel installation. These structures are strong enough to support the entire weight of a solar setup. Compared to other mounting and racking varieties, these are the most convenient gear for the panel.
These mounting options can also help affix the solar power system to a moving vehicle such as an RV.
Ground mounts
These are the adjustable mounting choices for solar panel setup on the ground. These structures are attached on top of concrete to ensure a stable foundation. However, you can change the alignment and angle as per the descent of sunlight and weather changes.
Since these mounts require huge spaces for installation, they are more commonly seen in commercial settings.
Pole mounts
These mounts are the most space-optimising choices for installing solar power setups. As the name suggests, these mounting structures comprise poles attached to the panels.
The foundation on which the poles are installed is not movable as they’re made of concrete. However, using a tracking system, you can adjust the poles’ direction based on insolation descent.

Component 4: Solar Batteries
Solar panels generate electricity, which must be stored for usage after sunset. Moreover, these battery banks are important if you intend to send the electricity surplus to a grid-tied system. That’s where batteries come into the picture. Electricity consumption decides the capacity and the number of batteries you require in the solar power setup. In addition, you can also utilise series, parallel or parallel-series combinations of battery banks depending on the generated power and weather conditions.
Since the overall cost of batteries can be high, the expenses with each solar setup depend on several factors, such as:
- Usage duration
- Type of solar battery
- Number of batteries in a setting
Based on the ion constituent of the battery banks, they come in various forms, including lithium-ion, nickel cadmium-ion, lead acid, and flow batteries. Even though lead acid batteries are the oldest kind, lithium-ion is the most used battery option nowadays due to its reliability and storage capacity.

Component 5: Charge Controllers
It is the most significant part of your solar power setup if the entire structure carries a battery. These components regulate the flow of electricity from solar panels to a battery.
The main objective of these intermediaries is to ensure that the power banks in the solar setup are charged to an optimum level. Maintaining proper capacity ensures the longevity of the batteries and prevents any mishaps.
These charge controllers are of two kinds:
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
The charge controller enables the batteries to receive peak power voltage for faster recharge with minimum losses.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
These charge controllers ensure that the batteries are not overcharged by modulating the duty cycle of electricity transfer with pulses.
Component 6: Solar Power Meter
A solar power meter is optional as it allows you to see the power consumption in your household.
This equipment is especially beneficial in net metering solar systems for excess electricity generation. With its installation, you can analyse how much surplus you can send to grid-tied banks. In addition, it enables you to observe any power leakages to gain the maximum efficiency of your solar power system.
Case Study: Optimising a Residential Solar Power System
Background
At Solar Panels Network, we pride ourselves on delivering customised solar solutions that maximise energy efficiency and sustainability. In this case study, we explore a recent residential project where we designed and installed a solar power system tailored to the unique needs and environment of the property. The project aimed to significantly reduce the homeowner’s reliance on the national grid and lower their electricity bills.
Project Overview
The homeowner sought a sustainable solution to reduce energy costs and decrease their carbon footprint. The property, located in a suburban area with ample sunlight, provided an ideal setting for a solar power system. Our team conducted a thorough site assessment to determine the best system configuration, considering factors such as roof orientation, space availability, and energy consumption patterns.
Implementation
To ensure optimal performance and efficiency, we implemented the following components:
- Solar Photovoltaic Panels: Installed 20 monocrystalline panels, known for their high efficiency and durability, to maximise energy capture and conversion.
- Solar Inverters: Deployed a string inverter with power optimisers to enhance system efficiency, especially given the partial shading from nearby trees.
- Racking and Mounts: Utilised robust, corrosion-resistant roof mounts to secure the panels, ensuring stability and longevity.
- Solar Batteries: Integrated a lithium-ion battery bank to store excess energy generated during the day, providing a reliable power source during nighttime and cloudy conditions.
- Charge Controllers: Installed Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controllers to optimise battery charging and protect against overcharging.
- Solar Power Meter: Implemented a solar power meter to monitor energy production and consumption, allowing the homeowner to track savings and system performance.
Results
- Increased Energy Independence: The system reduced the homeowner’s reliance on the national grid by 75%, resulting in significant energy cost savings.
- Optimised Energy Utilisation: The integration of solar batteries and a power meter allowed for efficient use of stored energy, even during peak usage times.
- Environmental Impact: The system contributed to a substantial reduction in the household’s carbon footprint, aligning with the homeowner’s sustainability goals.
Summary
The successful implementation of a customised solar power system at this residential property underscores the importance of selecting the right components tailored to specific needs and conditions. By choosing high-quality solar panels, efficient inverters, and robust battery solutions, we delivered a system that not only meets but exceeds the homeowner’s expectations. At Solar Panels Network, we continue to provide innovative and sustainable energy solutions, helping our clients transition to greener, more cost-effective power sources.
Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About the Main Components of a Solar Power System
Understanding the different types of solar panels, such as monocrystalline and polycrystalline, is crucial. Each type has unique benefits, and choosing the right one can significantly impact the efficiency and output of your solar power system.
Senior Solar Engineer
The role of solar inverters cannot be overstated. They are the heart of the solar system, converting DC to AC, which powers our homes. Opting for microinverters or power optimisers can maximise efficiency, especially in areas prone to shading.
Lead Solar Installation Specialist
Selecting the right solar batteries and charge controllers ensures that the energy harvested is efficiently stored and used. This is particularly important for systems that are off-grid or in areas with frequent power outages.
Solar Systems Consultant
Discover the Power of Solar with Solar Panels Network
Are you navigating the world of solar installations? Look no further than Solar Panels Network, the UK’s trusted partner in harnessing the sun’s potential. Our dedication goes beyond just installations; we’re on a mission to transform how homeowners and businesses across the UK perceive and utilise energy. By choosing us, you’re reducing your carbon footprint and making a smart financial move that promises savings for years ahead. Contact us today and embark on your solar journey.
Final Thoughts
Solar power systems’ cost-friendliness and sustainability are slowly becoming the most preferred choice for electricity generation. Solar energy is extremely beneficial for all, from residential DIY setups to commercial installations.
Depending on the kind of your project and the amount of electricity required, you need to make well-informed selections of its components. The quality of each constituting part decides the overall output from the solar power setup. Moreover, the region, environment, sunshine hours and load requirements also impact the performance of your solar energy system.
With these factors in mind, you must delve deeper into the utility of each component to understand how it will impact the output. The investment behind each part requires adequate consideration to attain the performance, production and convenience you aim to receive with the renewable energy panel setup.
About the Author
Solar Panels Network stands at the forefront of solar energy solutions, driven by a team of seasoned solar engineers and energy consultants. With over decades of experience in delivering high-quality solar installations and maintenance, we are committed to promoting sustainable energy through customer-centric, tailored solutions. Our articles reflect this commitment, crafted collaboratively by experts to provide accurate, up-to-date insights into solar technology, ensuring our readers are well-informed and empowered in their solar energy decisions.