Solar energy is a game-changer, and its undeniable benefits have revolutionised how we power our homes. The key to harnessing the full potential of solar panels lies in the solar inverter, a vital component that seamlessly transforms sunlight into usable electricity.
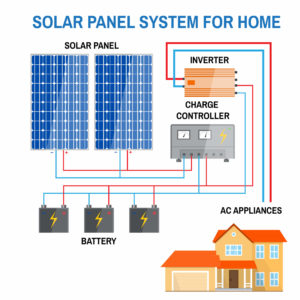
Here’s the essential insight: solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, while our households primarily operate on alternating (AC) power. To bridge this gap, a solar inverter transforms the DC power from the panels into the AC power our homes crave. So, if you’re contemplating switching to solar energy, the critical question becomes: how do you choose the perfect solar power inverter for your system? In this article, we’ll explore the various types of solar inverters available and guide you in making the right selection. It’s time to shed light on this vital component of your solar journey.
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Grid-Tied Solar Inverters
- 3 String Inverter
- 4 Solar Micro Inverter
- 5 Micro Parallel Inverter
- 6 Off-Grid Solar Inverters
- 7 Selecting A Solar Inverter
- 8 Hybrid Solar Inverters
- 9 Types Of Solar Inverters Based On The Output Wave
- 10 Case Study: Optimising Solar Power Conversion with the Right Inverter
- 11 Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About Solar Panel Inverters
- 12 Discover the Power of Solar with Solar Panels Network
- 13 Endnotes
Key Takeaways
- Solar Panel Inverters are crucial in converting solar-generated DC electricity into usable AC electricity for homes and grids.
- Different solar inverters with distinct advantages and disadvantages include Grid-Tied, String, Solar Micro, Micro Parallel, Off-Grid, and Hybrid Inverters.
- The type of solar inverter you choose should depend on load requirements, power capacity, solar array specifications, and the need for grid connection or off-grid independence.
Grid-Tied Solar Inverters
A grid-tied inverter system converts DC voltage from the solar array into AC voltage. This power can either be used immediately or exported to the utility grid.
Grid-tied inverters are highly efficient, and installing them is a straightforward process. However, a grid inverter only works when the utility is on.
Most grid-tied inverters use the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology. This feature milks the maximum power possible from the solar PV array.
If you have a direct connection, the AC power produced by the solar panel system is sent to the utility grid. Conversely, if your connection is through the building’s grid, the AC power is consumed by your appliances first, and then the remainder is sent to the utility grid.
String Inverter
String inverters, or central inverters, treat the solar array as a single solar panel. They are quite popular because of their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
The primary concern with string inverters is that even if one of the array’s panels is hampered by shade or degradation, the entire array’s performance is impacted. Consequently, the inverter’s DC input power reduces, reducing AC power.

Solar Micro Inverter
Solar micro-inverters, or module inverters, have a comparatively low output power, typically less than 250 W. These inverters are a part of the solar system and function as a central inverter exclusively for the solar panel they are connected to.
Micro-inverters are installed on every array panel, so the overall cost is usually high. However, this arrangement resolves the drawbacks of string inverters, as the malfunctioning of one panel does not disrupt the entire solar power system.
A micro inverter also uses MPPT to monitor the performance of solar panels and ensure that it squeezes maximum power from the panels.
Micro Parallel Inverter
Micro-parallel inverters are a relatively new technology combining the positives of both string and micro-inverters.
This inverter is a smart device consisting of four distinct channels connected to four solar panels. Each of these channels works as a micro-inverter and can track the performance of its solar panel using MPPT.
The micro parallel inverter is also a string inverter for the four solar panels. However, if one panel fails, the other will not suffer.
Off-Grid Solar Inverters
Off-grid systems allow you to live and work wherever you want since you can generate your electricity and live independently. The primary function of an off-grid inverter is to convert the output voltage of the solar array or the battery bank to AC voltage.
Not every off-grid solar system requires an inverter. If only DC loads have to be powered, off-grid inverters are not needed.
An off-grid inverter can be directly connected to the solar array and provide AC electricity to the AC loads or connected to a backup inverter connected to battery storage directly or via a DC breaker.
Selecting A Solar Inverter
Picky a solar inverter can be tricky since the markets are flooded with many options.
We have curated a cheat sheet to help you find the best inverter for your needs.
For Off-Grid Solar Inverters
These inverters have many specifications you need to consider before making a choice.
Let us discuss some of the key factors that you need to look at.
Output Voltage And Frequency
It is based on your load requirements and is typically the same as the standard supply voltage and frequency across the country.
Output Power
The power capacity of an off-grid inverter should be about 110 to 120% of your load’s total power capacity.
You can calculate the load’s total capacity by adding the power consumption of all your loads, considering the inductive loads with surge current, and oversizing to avoid underestimation.
Built-in solar Charge Controller
The built-in solar charge controller can be MPPT or PWM (pulse width modulation).
Technically, MPPT is better since it can convert solar panels’ high voltage to lower voltage, charging batteries with low losses and high efficiency. However, it costs much more than the PMW type.
If you can size your PMW solar charge controller according to the specs of your solar panel, it will work just as well as MPPT.
Solar Array Maximum Output
The maximum DC output voltage of the OV system should not be greater than the maximum DC input voltage of the inverter.
Battery Charger Output
Several off-grid solar inverters include battery chargers used to recharge batteries and a backup generator. Ideally, the charger should be in the range of 50 to 100 amps DC.
Efficiency
Efficiency measures how much power your inverter delivers to your home from the batteries under perfect conditions. A peak efficiency rating should ideally be between 94% to 96%.
For Grid-Tied Solar Panels
If you are looking for a grid-tied inverter, consider the following factors.
- The minimum voltage of the solar array should be lower than the inverter’s maximum input voltage (DC).
- The PV array’s working voltage range should be within the MPPT voltage range of the inverter.
- The inverter’s output power should be 0.9 to 0.95 of the solar array’s peak power.
- The inverter’s minimum allowable system voltage should be lower than the PV array’s minimum DC voltage.
- The PV array’s maximum current should be less than the maximum input DC.

Hybrid Solar Inverters
A hybrid solar inverter combines the features of a standard solar inverter and a battery inverter. It is an affordable device with a smart charging electricity routing unit.
Hybrid systems consist of more inputs and outputs than a traditional string inverter. They simplify moving electricity between your fuse box, the grid, and the energy storage unit.
Let us look at the various pros and cons of solar hybrid inverters.
Advantages Of A Solar Hybrid Inverter
- These inverters integrate charge controlling, performance monitoring, and bi-directional inverter functions within an affordable package.
- They have built-in charge controllers that detect the best time to send electricity from your battery bank to the grid.
- Many such inverters allow you to send your system performance data to a cloud portal by the company for monitoring and control.
- DC-coupled hybrid inverters take DC power from the solar panels and feed it directly to your battery bank without converting it to AC power.
- Some inverters enable you to connect a smaller inverter with your solar array or a larger array to your solar inverter.
Disadvantages Of A Solar Hybrid Inverter
- Some inverters may not have the feature to use the electricity generated from your panels when the grid is down.
- Higher-performance hybrid inverters are typically designed for indoor installations and may not be IP65-rated, which means they are not weather-resistant.
- If you already own a working solar panel system and want to add battery resilience, hybrid inverters may not be the best choice for your solar systems.
Types Of Solar Inverters Based On The Output Wave
Solar inverters can be classified into three categories based on the type of output wave produced.
Pure Sine Wave Inverter
Pure sine wave inverters are expensive since they produce AC power similar to actual sine waves provided by the grid. A pure sine wave is steady and continuous, providing periodic and smooth oscillation.
These inverters have the highest functionality because they can run any equipment designed to work on a pure sine wave.
The following devices will work exclusively on a pure sine wave inverter. They might get damaged if you try to run them on other inverters.
- AC devices such as compressors, microwaves, or refrigerators.
- Audio and video equipment
- Certain medical equipment
- Satellite systems
If you are considering installing solar panels on your roof or RV, you should explore this option. Pure sine wave inverters convert DC to AC and bring the voltage up to the grid level.
Square Wave Inverter
Square wave inverters, or modified sine wave inverters, are perhaps the simplest inverters. They are suited to run simple tools and equipment with universal motors but nothing beyond that.
Such inverters are digital inverters and generate square-wave AC output. Nowadays, a modified sine wave inverter is not as common.
You can only find old or cheap versions. Square wave inverters produce very loud noises and are not entirely reliable, so it does not come as a surprise that their popularity has declined.

Quasi Sine Wave Inverter
Quasi-sine wave inverters, also known as stepped-sine wave inverters, are not easily accessible in the market. These inverters are low-cost solutions for running electronic gadgets such as computers.
Stepped sine wave inverters may also create additional noise, like square inverters. Moreover, they are unsuitable for devices such as microwave ovens, vacuum cleaners, mobile phones, computers, etc.
Case Study: Optimising Solar Power Conversion with the Right Inverter
Background
A family in Bristol, aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills, decided to install a solar PV system on their home. With limited roof space and concerns about shading from nearby trees, they needed a solution that maximised the energy output from their solar panels. The goal was to select an inverter that could handle these challenges efficiently while providing reliable power conversion.
Project Overview
The project involved selecting and installing a solar inverter that could optimise the performance of the solar panels, despite potential shading issues. The homeowner also wanted the flexibility to possibly expand the system in the future, either by adding more panels or integrating battery storage.
Implementation
- Assessment and Planning: We conducted a detailed assessment of the property’s solar potential, including an analysis of potential shading and the overall energy needs of the household. This information guided the selection of the most suitable inverter type.
- Inverter Selection: Given the shading concerns and the desire for high efficiency, we recommended a system with micro-inverters. Unlike string inverters, micro-inverters optimise the output of each individual panel, ensuring that shading on one panel does not reduce the performance of the entire system.
- Installation: The micro-inverters were installed on each solar panel. This setup allowed for individual monitoring of each panel’s performance, providing the homeowner with detailed insights into their energy production. The installation also included a monitoring system accessible via a smartphone app, offering real-time data on energy generation and consumption.
- Future Proofing: The system was designed to be easily expandable. If the family decides to add more panels or integrate a battery storage system in the future, the micro-inverters will allow for seamless integration without needing significant modifications to the existing setup.
Results
- Maximised Energy Output: The micro-inverters effectively mitigated the impact of shading, ensuring that each panel produced the maximum possible energy. This optimisation resulted in higher overall energy production compared to a traditional string inverter setup.
- Cost Savings and Efficiency: The family reported significant savings on their electricity bills, thanks to the efficient conversion of solar energy into usable electricity. The micro-inverters’ high efficiency also meant that the system had a quick return on investment.
- Detailed Monitoring and Control: The monitoring system provided the family with real-time data on their energy production and consumption, enabling them to manage their energy use more effectively. This feature also allowed for quick identification and resolution of any issues, ensuring the system operated at peak efficiency.
- Environmental Impact: By switching to solar power, the family significantly reduced their reliance on fossil fuels, lowering their carbon footprint. The system’s efficient design further enhanced its environmental benefits by maximising the use of renewable energy.
Summary
This case study demonstrates the importance of choosing the right inverter to optimise solar energy production, especially in scenarios with potential shading or limited roof space. The use of micro-inverters provided the family with a highly efficient and expandable solar power system, maximising their energy savings and reducing their environmental impact. At Solar Panels Network, we are committed to offering tailored solutions that meet our clients’ specific needs, ensuring they can fully harness the benefits of solar energy. This project underscores our expertise in selecting and installing the most suitable inverters for diverse solar installations.
Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About Solar Panel Inverters
Selecting the right solar inverter is crucial for maximising the efficiency of your solar energy system. Inverters are responsible for converting DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used in your home. The choice of inverter—whether grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid—depends on your specific energy needs and whether you want to be connected to the grid or independent.
Senior Solar Installer
Micro-inverters and string inverters each have their advantages. Micro-inverters are ideal for systems where shading might affect only some panels, as they optimise each panel individually. On the other hand, string inverters are more cost-effective and are suitable for installations where shading is not an issue.
Renewable Energy Consultant
Efficiency and durability are key factors when choosing a solar inverter. High-quality inverters not only convert energy more efficiently but also last longer, providing a better return on investment. It’s also important to consider the warranty offered, as this can provide peace of mind and protect your investment over the long term.
Lead Solar Technician
Discover the Power of Solar with Solar Panels Network
Are you navigating the world of solar installations? Look no further than Solar Panels Network, the UK’s trusted partner in harnessing the sun’s potential. Our dedication goes beyond just installations; we’re on a mission to transform how homeowners and businesses across the UK perceive and utilise energy. By choosing us, you’re reducing your carbon footprint and making a smart financial move that promises savings for years ahead. Contact us today and embark on your solar journey.
Endnotes
Understanding solar panel inverters is not an easy task. You will have to familiarise yourself with a lot of technology.
Buying a solar inverter is not just about deciding whether you want to get an off-grid system, be tied to the grid, or adopt a hybrid model. You also have to look at the other details discussed above.
Regardless of the time and effort involved in zeroing in on a solar inverter, the process is worth it. Switching to solar electricity lowers your electricity bills and is also great for the environment.
About the Author
Solar Panels Network stands at the forefront of solar energy solutions, driven by a team of seasoned solar engineers and energy consultants. With over decades of experience in delivering high-quality solar installations and maintenance, we are committed to promoting sustainable energy through customer-centric, tailored solutions. Our articles reflect this commitment, crafted collaboratively by experts to provide accurate, up-to-date insights into solar technology, ensuring our readers are well-informed and empowered in their solar energy decisions.