As our world continues to evolve, so do our efforts towards a more sustainable future. Solar panels have emerged as a solution for those seeking to reduce their environmental impact while saving money on energy costs. In today’s age of innovation, it’s no surprise that this technology has become increasingly popular among homeowners and businesses alike.
With solar energy, you have the power to create a cleaner, healthier world for generations to come. This comprehensive guide is your key to unlocking the full potential of solar panels. It provides valuable insights into solar panels’ advantages, disadvantages, types, and installation processes, empowering you to make informed decisions and embark on a journey toward a greener, more sustainable future. Whether you’re considering your first solar installation or seeking to optimise your existing system, this resource serves as your ultimate guide to solar panels. So let’s take a deep dive into the world of solar energy and discover how you can contribute to a better world!
Contents
- 1 Advantages of Solar Panels
- 2 Disadvantages of Solar Panels
- 3 Types of Solar Panels
- 4 Other Types of Solar Cells
- 5 How Do Solar PV Panels Work?
- 6 Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
- 7 How to Pick the Best Solar Panels
- 8 How Many Solar Panels do you need?
- 9 Solar Panel Installation
- 10 How Much do Solar Panels Cost?
- 11 Case Study: Comprehensive Solar Panel Installation for a Residential Property
- 12 Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About Solar Panels
- 13 Discover the Power of Solar with Solar Panels Network
- 14 Finishing Notes
Advantages of Solar Panels
Check out these advantages if you’re on the fence about installing a solar panel system for your property.
1. Save on Electricity Bills
With the large number of electrical appliances that we use today, electricity bills can burn a sizeable hole in our pockets. By using solar energy, you can reduce your utility bills to a large extent.
You don’t just get free energy; you can also sell the surplus energy produced to the national grid and earn some returns on your investment.
2. Reduce your Carbon Footprint
Traditional energy sources, such as coal, oil, and fossil fuels, release harmful substances like oxides of carbon, nitrogen and Sulphur. These are highly potent gases and lead to air pollution and global warming.
You can offset this environmental impact by switching to solar energy for domestic electricity consumption. Solar energy generation does not release any toxic gases, and domestic solar panels can potentially offset about 25 tons of carbon dioxide over their lifetime.

3. Round-the-year Energy
It is a misconception that solar panels need heat to be effective and are not valuable during winter.
Solar panels harness sunlight, not heat. Although they function best during the summer, they work well during the winter months and even on cloudy days.
4. Minimal Maintenance Required
Solar panels require very little maintenance. On average, they last for 25 to 30 years without technical hassle.
However, it would be best to clean your solar panels regularly for their efficient working. You should also ensure they do not collect dirt, branches, etc. For this, schedule regular inspections for your system, and you should be ready for months at a stretch.
5. Independence From the Grid
You can integrate solar batteries into your solar panel system to store energy for nighttime, rainy days, or during a power outage. This way, you can be completely independent of the National Grid.
Installing a battery is especially helpful if you live in areas where extending power lines is not feasible.
6. Renewable Sources of Energy
Since the sun’s energy will not run out soon, it can be considered a renewable energy source. Moreover, you can store this energy to get free electricity even when the sun is not around.
7. No Permit Required
You do not need prior permission to install solar panels. While some rules and regulations are in place, they are pretty minor.
8. Increases Your Property Value
Solar panels are an excellent investment if you want to increase the market value of any real estate. A property with a solar panel system can command a higher price than one without it in the current market conditions.
Disadvantages of Solar Panels
There are a few downsides to installing solar panels on your property. Some of them are listed below.
1. Dependent on Weather
Although solar panels work on dark or rainy days, they lose much of their efficiency. If you are not connected to the grid, you’ll have to store energy in a battery backup for such situations.
2. High Initial Investment
Upfront, solar panels can be a little expensive. However you earn your money back over time, but it can take a few years.
3. Dependence on Surrounding Structures
Incorrect placement of solar panels can seriously hamper their effectiveness. Typically, panels with large buildings or tall trees around them function well. Solar panels might not be the best option if you live in such an area.
These are the most common downsides of installing a solar power generation system on your property. However, its pros greatly outweigh the cons, making it a worthwhile investment.
Types of Solar Panels
A solar panel is a device that absorbs the sun’s energy and converts it into electricity. These panels are made of photovoltaic (PV) cells that use semiconductor technology to convert the sun’s energy into usable electricity.
Over time, there have been countless improvements to solar cells and panels. Let us explore the different types of solar panels available today.
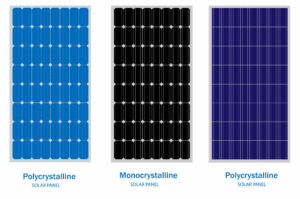
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are the earliest form of solar panels and the most developed ones so far.
“mono” means single, and “crystalline” refers to the crystal, indicating that these panels are made of single-crystal silicon solar cells. Because of their composition, these cells offer higher output.
Pure silicon is formed into bars and sliced into wafers to make monocrystalline solar cells. During this process, the edges of the cells are cut, smoothened, and rounded to increase the efficiency of the cells.
Monocrystalline cells appear black due to light interacting with the pure silicon crystal. However, their back sheets and frames can be found in various colours. Typically, their back is black, white, or silver, and the metal frame is silver or black.
These panels generally offer the best efficiency and power capacity among other solar panels available.
Advantages of Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- They perform well even in low levels of sunlight.
- They are space-efficient.
- They are made with pure, high-quality silicon.
- They are long-lasting.
- They have a higher power output.
Disadvantages of Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- They are the most expensive kind of solar cells.
- Plenty of waste is produced during their production.
- The performance of these panels suffers when the temperature goes up.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels, or multi-crystalline solar panels, are mid-range solar panels. They are not as effective as monocrystalline panels but are more affordable.
These panels consist of several fragments of silicon crystals melted together. This process of creating such panels lowers their efficiency and reduces lifespan. This is because the electrons get less freedom to move around since there are many crystals in each cell.
To make these panels, raw silicon is melted and poured into square moulds to create wafers. Unlike monocrystalline cells, these edges do not have to be cut, reducing waste. The wafers are then assembled to create polycrystalline solar panels.
These panels have a blue hue because of how light reflects off the silicon fragments of the cell. Popular back sheet colours for polycrystalline panels are white and silver, while the frames are typically silver.
The efficiency of these cells is typically between 15% and 17%, and their wattage is lower than that of monocrystalline cells.
Advantages of Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- The manufacturing process is faster.
- There is not a lot of waste during production.
- They are more affordable compared to monocrystalline solar panels.
Disadvantages of Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- They have a lower efficiency rate and shorter life span.
- They are not very space-efficient.
- They are not tolerant of high temperatures.
3. Thin-Film Solar Panels
As the name suggests, these panels consist of extremely thin cells. Its cells are about 350 times thinner than the wafers used in monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
These panels are manufactured using layers of semiconducting materials, like silicon, copper indium gallium selenide, and cadmium telluride. The layer of semiconductors is placed between the conducting and transparent layers and topped with thin glass, which helps trap sunlight.
These non-crystalline panels generally have lower efficiency (close to 11%) and power capacity than crystalline variants. They require plenty of roof space to generate larger amounts of energy.
Although thin-film solar panels are quite flexible, they degrade faster than crystalline panels. However, because of their flexibility, they can be moulded into different shapes, like shingles or tiles, to suit various applications.
The colour of thin-film panels could be blue or black, depending on their manufacturing material. Since they tolerate high temperatures, they are an excellent choice for tropical countries.
Advantages of Thin-Film Solar Panels
- They are the most affordable kind of solar panels.
- They can tolerate very high temperatures.
- They are highly flexible.
Disadvantages of Thin-Film Solar Panels
- They are not very efficient.
- They have a short life span.
- They take up a lot of space.
Other Types of Solar Cells
Besides the three main kinds of solar panels listed above, two other less common solar cell options exist. They are:
1. Amorphous Silicon Solar Cells
Amorphous silicon cells are the most recent development in the solar cell industry. They are made of amorphous silicon, and the atoms are not ordered in a crystal lattice pattern.
Silicon is deposited in an extremely thin layer on a backing substrate to produce these cells. At times, numerous silicon layers are deposited in slightly different ways to respond to varying wavelengths of light and are laid on each other to enhance efficiency.
Advantages of Amorphous Silicon Solar Cells
- They are mass-produced and lead to cost efficiency.
- They can be flexible.
- They can perform well even with lower light levels.
Disadvantages of Amorphous Silicon Solar Cells
- They are not as space-efficient as crystalline panels.
2. Bio-hybrid Solar Cells
A bio-hybrid solar cell is formed by combining organic and inorganic matter. These cells were first created when a team recreated photosynthesis using Photosystem I for better solar energy conversion efficiency than regular PV cells.
When several layers of Photosystem I are put together, they convert the energy collected into chemical energy, resulting in current passing through the cell.
Advantages of Bio-hybrid Solar Cells
- They are far more efficient than any other kind of cell.
- The production process is relatively cheap.
- No power is lost during the conversion of chemical energy to electrical power.
Disadvantages of Bio-hybrid Solar Cells
- They have a shorter lifespan.
 How Do Solar PV Panels Work?
How Do Solar PV Panels Work?
Solar PV panels consist of numerous tiny photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. These cells are made of semi-conductive materials, typically silicon, that enable them to conduct electricity while maintaining the electrical imbalance required to create an electric field.
As sunlight comes in contact with the semiconductor in PV cells, solar energy is absorbed in photons. It knocks electrons loose, allowing them to drift freely within the cell.
Solar PV cells are carefully designed with negatively and positively charged semiconductors packed together to form an electric field. The field compels the freely moving electrons to flow towards the conductive metal plates lining the cell.
This is called an energy current, and its strength determines the amount of electricity each cell can produce. As soon as the loose electrons strike the metal plates, the current is directed into the wires, enabling electrons to flow as they would in any other mode of electricity generation.
The Flow of Energy
When the solar panels generate electric current, energy passes through a series of wires into an inverter. The energy generated by solar panels is DC electricity, while most of us need AC electricity to power our buildings.
An inverter is thus required to transform the electricity from DC to AC and make it useable.
When electricity is changed into AC form, it is sent from the inverter to the breaker box, also known as an electrical panel. From there, it gets distributed throughout the building and can power appliances, lights, etc.
Where Does The Unused Electricity Go?
The electricity consumed through the electrical panel is then directed to the utility grid via the utility meter. It is a device that measures the flow of electricity from the grid to your house and vice versa.
If your solar energy system produces more electricity than you consume, the meter runs backwards, and you get credited for the excess electricity you generate via net metering.
Unless you are entirely off-grid with an energy storage solution, you must take electricity from the utility grid when your solar panels are not producing energy, for instance, at night.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
You must keep a few things in mind to maximise your investment in your solar electricity generation system and get the best returns. Maximise your solar panel efficiency with these tips and tricks.
1. Location, Angle, and Direction
You must install the PV system at an angle so solar cells can capture as much sunlight as possible. The United Kingdom receives excellent sunlight from 9 AM to 3 PM.
The panels should be well exposed to sunlight during this period. Moreover, the angle of your roof will also play a role in sun exposure. Ideally, solar panels should be south-facing to be exposed to sunlight for the longest time.
A study published by Stanford University suggests that a tilt angle of 34 degrees is the best placement position for solar panels in the United Kingdom.
You can install brackets if your roof is not oriented according to the angle. However, this adjustment needs to be assessed by a certified MCS installer.
2. Maintenance
Maintenance is essential for maximising the lifespan of your solar panels. The panels generally last 25 to 30 years and require very little maintenance. It would be best to get the panels checked occasionally by your installer or any other certified service provider.
You can even ensure that your panels are always clean by yourself. It will involve removing branches and leaves from your panels and rinsing them with a hose.
Be careful not to touch or sponge your panels while cleaning.
3. Roof Suitability
Before installing solar panels, you must ensure your roof is strong enough to support the system’s weight.
For instance, a 4 kW system typically consists of 16 panels of 250W, making the total weight close to 280kg.
The material of your roof is also important to consider. While most materials can handle solar panels comfortably, slate and wooden roofs might be too brittle. Moreover, your roof must be large enough to fit the solar panels.
You need about 30 cm of space around the panels, so a 4 kW system requires at least 29 sq.m. of roof area.
4. Size of the Solar Panel System
As a rule of thumb, the bigger your solar panel, the more electricity you generate. Calculating your electricity needs is the best way to determine your size requirement.
Monocrystalline panels are your best choice if you’re on a space crunch. These panels are highly efficient and require comparatively fewer panels to generate energy.

How to Pick the Best Solar Panels
It would be best to consider several factors when looking for the best solar panels for your property. These include:
1. Type
The three main panels available today are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin film. You can choose the best option depending on your energy requirements and budget.
2. Efficiency
The efficiency of a solar panel measures how much energy from the sun can be converted into usable electricity. It is calculated as a percentage. Domestic solar panel systems usually have an efficiency of around 15% to 20%.
3. Power
Power refers to the energy output of a solar panel system under Standard Test Conditions. You can measure the power of a solar panel in watts (W).
4. Power Tolerance
Power tolerance refers to how much your solar panel system can deviate from its stated power (in watts). The variance can be expressed in watts or percentages.
For instance, if a 200W panel has a power tolerance of +4% / -0%, its power output can vary between 200W and 208W under regular conditions.
5. Size
If you have limited roof space, you’ll have to be extremely careful with the placement of your panels. Ensure enough space to fit the entire system and leave extra room for movement.
6. Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient shows the percentage decrease in power output for every 1 °C increase in temperature after 25°C. It is essential to know how much your solar panels will be affected by a rise in the temperature.
7. Weight
The weight of your solar panels will depend on the strength of your roof. If your roof is not robust, you must look for lightweight panels.
8. Performance Degradation
While the lifespan of a solar panel is typically between 25 and 30 years, the panels will experience some wear and tear over time.
Generally, there is a 2-3% decline in efficiency after the first year and 0.2-0.7% every following year.
9. Product Warranty
Try to get your hands on a product that offers a maximum warranty. A warranty shows the manufacturers’ confidence in their products. Warranties for solar panels typically range from between 10 years to 25 years.
10. Wind Tolerance
Since we’re talking about setting up solar panels in the UK, we must consider strong winds and hurricanes. You want your solar panels to be able to tolerate such harsh conditions.
Manufacturers typically test tolerance and record it in pascals (Pa). The higher the figure, the more is their tolerance. Most panels can withstand up to 2400 Pa, which is almost equal to 140 mph.
How Many Solar Panels do you need?
Each household has its own unique power consumption needs. It would be best to look at your electricity bills to determine your power consumption in kWh.
You could either calculate month by month or take the sum of monthly or quarterly figures to determine an annual estimate. Then, deciding what percentage of your bill you want to cover with a solar panel system would be best.
You must also calculate the number of panels that can fit on your roof. On average, a solar panel takes almost 1.44 sq.m. roof space. While assessing roof space, you must leave at least 30 cm from the edge.
A 4 kW solar panel system would typically require about 16 solar panels with a power output of 250W. Likewise, a 5 kW system will consist of 20 solar panels.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Requirement
The following factors play a role in determining the number of solar panels you need to power your property.
- Your roof capacity.
- Your electricity consumption.
- The number of sunshine hours.
- How much of your total power consumption will you cover with solar energy?

Solar Panel Installation
Setting it up after zeroing on a solar panel installer takes only a few days.
Let us quickly run through the steps.
1. Install the Scaffolding
Scaffolding has to be erected around the house to ensure the safety of the installation team.
2. Set Up Roof Anchors
Roof anchors are required to hold the base of the solar panels. Different kinds of anchors are available, and they are chosen depending on the type of tiles on your roof.
3. Attach the Frame
The frame comprises aluminium bars and is required to keep the solar panels in place. All the bars should be fitted in the same direction, parallel.
The structure should be slightly tilted anywhere between 18 to 36 degrees.
4. Erect the Panels
The installation team will clamp the solar panels to the aluminium frame. At first, they are set up loosely to leave room for adjustment. After all the panels are positioned, they are tightly secured to the aluminium frame.
5. Wire the Panels
The electrical wiring of the panels depends on the amperage, voltage, and power of the solar panel system. Generally, universal connectors like the MC4 are perfect for wiring because of their versatility. The panels can either be connected in series or parallel connections.
6. Connect to a Solar Inverter
A solar inverter is a part of the solar array that converts the energy captured into AC electricity for use by household appliances. To connect the solar panel system to the inverter, you must join the panel’s positive wire to the positive terminal and the negative wire to the negative terminal.
7. Connect to a Solar Battery and the National Grid
While connecting the solar inverter to the grid is crucial, you also need a solar battery to store backup electricity when you don’t want to depend on the grid.
Installers take a standard plug to connect to the main switchboard and an output wire to connect to the electric board.
For connecting the solar inverter to the battery, the battery’s positive terminal and the inverter’s positive terminal are connected, and the same is done for the negatives.
8. Turn on The Inverter
Once everything is set up, you can turn on the inverter to use clean energy!
How Much do Solar Panels Cost?
A domestic solar panel system costs anywhere between £5,000 to £10,000. This cost varies based on the number of panels, depending upon your energy consumption.
Going for a more extensive solar panel system will be more expensive, but it will generate more electricity and increase your savings. With the UK government offering financial incentives for domestic solar panel installation, the high installation costs are covered in the long run.
Solar Panel Prices for Different System Sizes
A small house with up to three residents should be able to cover their electricity needs with a 3 kW solar panel system, which will cost about £5,000 to £6,000.
A 4 kW system will be ideal for a three- to four-person household, costing about £6000 to £8,000.
Larger homes with more than four residents would need a 6 kW solar panel system that will cost about £8,000 or higher.
While these are some standard sizes, some providers even allow customisation. So, you can get the ideal size for your home’s electricity requirements and pay accordingly.

Grants for Solar Panels in the UK
The UK government encourages grants to homeowners to switch to cleaner sources of energy by providing them with the opportunity to earn via their solar panel systems, wind energy systems, etc.
Smart Exchange Guarantee (SEG)
Under the SEG, homeowners can supply surplus energy to the utility grid. In return, they will receive money for their export.
Everyone receives different tariffs depending on the electricity supplier. The suppliers can offer either fixed rates or flexible options.
Feed-in Tariff (FiT)
Under this incentive, households could export excess electricity to the grid to receive payments. The tariff consisted of two elements:
- A generation tariff for the total amount of electricity generated, calculated on a per-unit basis.
- An export tariff for the electricity exported to the grid is assumed to be half the total electricity generated.
The FiT scheme is no longer taking in new applicants.
Case Study: Comprehensive Solar Panel Installation for a Residential Property
Background
Solar Panels Network was approached by a homeowner in the UK looking to install a solar panel system. The client was interested in reducing their electricity bills and decreasing their carbon footprint. The property had ample roof space and received good sunlight throughout the day, making it an ideal candidate for solar energy generation.
Project Overview
The project’s goal was to install a solar panel system that met the homeowner’s energy needs while also providing the potential to sell excess energy back to the grid. The project included selecting the appropriate type of solar panels, designing the system layout, and ensuring optimal installation to maximise energy production.
Implementation
- Assessment and Design: Conducted a thorough site assessment to determine the best panel type and layout. Decided on monocrystalline solar panels for their high efficiency and space-saving benefits.
- Installation Process:
- Installed scaffolding to ensure safety during the installation process.
- Set up roof anchors and attached the aluminium frame to support the solar panels.
- Positioned and securely fastened 20 monocrystalline solar panels on the frame.
- Wired the panels and connected them to a solar inverter to convert DC to AC electricity.
- Connected the system to a solar battery for energy storage and to the National Grid for surplus energy sales.
- Post-Installation Support: Provided the homeowner with a maintenance guide and scheduled periodic inspections to ensure optimal system performance.
Results
- Energy Output: The system produced an estimated annual output of 8,000 kWh, covering nearly 80% of the household’s energy consumption.
- Cost Savings: The homeowner saw a significant reduction in electricity bills, with an estimated payback period of 6-7 years.
- Environmental Impact: The solar panel system reduced the household’s carbon emissions, aligning with the homeowner’s sustainability goals.
- Additional Benefits: The system’s connection to the National Grid allowed the homeowner to earn money by selling excess energy, further enhancing the financial benefits of the installation.
Summary
This case study illustrates the comprehensive approach taken by Solar Panels Network in designing and installing a solar panel system tailored to the specific needs of a residential property. From initial assessment to final installation and post-installation support, the project successfully met the client’s energy and environmental objectives. The results not only provided significant cost savings and environmental benefits but also highlighted the potential of solar panels as a sustainable energy solution for UK households.
Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About Solar Panels
Choosing the right type of solar panels can significantly impact your energy savings and efficiency. Monocrystalline panels, for instance, are ideal for those looking to maximise output in limited spaces.
Senior Solar Installation Specialist
Proper installation and orientation of solar panels are crucial for optimising performance. Ensuring panels face the correct direction and are free from obstructions can greatly enhance energy production.
Renewable Energy Consultant
Understanding the long-term benefits of solar panels, such as reduced electricity bills and environmental impact, is essential. Solar panels are an investment in both financial savings and sustainability.
Solar Energy Advisor
Discover the Power of Solar with Solar Panels Network
Are you navigating the world of solar installations? Look no further than Solar Panels Network, the UK’s trusted partner in harnessing the sun’s potential. Our dedication goes beyond just installations; we’re on a mission to transform how homeowners and businesses across the UK perceive and utilise energy. By choosing us, you’re reducing your carbon footprint and making a smart financial move that promises savings for years ahead. Contact us today and embark on your solar journey.
Finishing Notes
Solar energy is undoubtedly a boon to the environment. However, people have several concerns before installing a solar panel system at home.
We hope this guide answered your questions about solar panels, their types, working, etc.
Setting up solar panels is a good idea if you want to do your bit for the planet. Moreover, with the incentives available in the United Kingdom, its installation will not even burn a hole in your pocket.
Get your solar installation today!
About the Author
Solar Panels Network stands at the forefront of solar energy solutions, driven by a team of seasoned solar engineers and energy consultants. With over decades of experience in delivering high-quality solar installations and maintenance, we are committed to promoting sustainable energy through customer-centric, tailored solutions. Our articles reflect this commitment, crafted collaboratively by experts to provide accurate, up-to-date insights into solar technology, ensuring our readers are well-informed and empowered in their solar energy decisions.

 How Do Solar PV Panels Work?
How Do Solar PV Panels Work?